ANTLR4를 작년에 validator 만들 때 보고 그 뒤로 안보고 있었다.
물론 그때도 타입스크립트로 만든다고 공식 ANTLR4가 아닌 antlr4ts를 써서 공식 ANTLR4를 찾아본지는 꽤 오래 되었는데… 간만에 들어가보니 ANTLR4 명령어?가 파이썬 이용하는걸로 바뀌어서 기존에 jar파일 받아서 java -jar antlr4.ts 어쩌구 저쩌구가 훨씬 편해졌다….
그리고 antlr4ts는 서스테이닝이 안되고 있어서 하루빨리 버려야한다.
여튼 그러한 이유로 공식 ANTLR4를 써야하고, 새로운 ANTLR4는 다음과 같이 설치하면 된다.
$ python3 -m pip install antlr4-tools그래서 옛날에 했던 간단한 사칙연산 계산기를 다시 만들어 봅시다.
그리고 이번에는 요즘에 관심있게 보고 있는 deno를 사용해봅시다. 다음과 같이 deno 프로젝트를 초기화 한다.
$ deno init deno-antlr4그 다음 Calc.g4 파일을 만들어서 문법을 정의한다.
grammar Calc;
statement
: expression rest_expression*
;
rest_expression
: op=(PLUS | MINUS) expression
;
expression
: (term | neg_term) rest_term*
;
rest_term
: op=(ASTERISK | DIVIDE) term
| op=(ASTERISK | DIVIDE) neg_term
;
neg_term
: MINUS term
;
term
: number
| constant
| LPAREN statement RPAREN
;
number
: NUMBER
| SCIENTIFIC_NUMBER
;
constant
: PI
| E
;
PLUS: '+';
MINUS: '-';
ASTERISK: '*';
DIVIDE: '/';
NUMBER: [0-9]+ ('.' [0-9]*)?;
SCIENTIFIC_NUMBER: [0-9]+ ('.' [0-9]*)? ('e' | 'E') '-'? [0-9]+;
PI: 'π' | 'pi' | 'PI';
E: 'e';
LPAREN: '(';
RPAREN: ')';
WS: [ \n\r\t]+ -> skip;그 다음 타입스크립트 렉서와 파서를 만든다.
$ antlr4 -Dlanguage=TypeScript Calc.g4그러면 토큰, interp, 타입스크립트 코드 파일들이 생성된다.
다만 이렇게 만들어지는 파일들은 node기반이기 때문에 다음에 따라 코드 파일들을 수정한다.
- deno는 로컬 파일 import 시 JS인지 TS인지 확실히 해야한다. 따라서 로컬 파일을 import하는 부분에 모두 확장자를 명시해야한다.
- deno에서 npm 라이브러리를 사용하려면 라이브러리 앞에 npm: 을 붙여야한다. 버전을 명시하지 않으면 가장 최근버전을 가져온다.
그래서 대충 리스너 상단을 보면
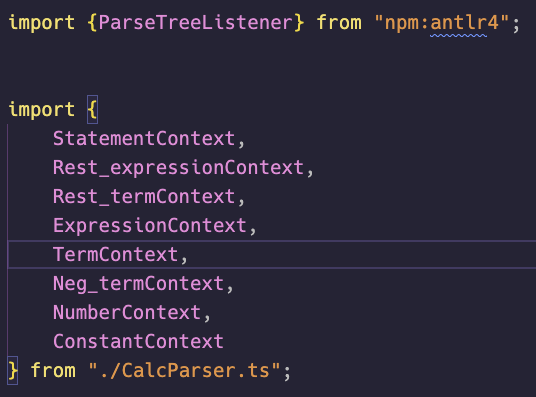
요런식으로 바꿔주어야 에러가 안난다.
그 다음 리스너를 구현한다. https://blog.naver.com/aosamesan/222203283616
이게 또 좀 다르네… antlr4ts에서는 ParseTreeListener의 메서드들이 ?로 선언되어서 구현 안해도 되었지만 antlr4 에서는 꼭 구현하도록 되어 있어서 안하면 에러가 난다… 그래서 코드가 아래와 같다.
import { ErrorNode, ParserRuleContext, TerminalNode } from "npm:antlr4";
import CalcListener from "./CalcListener.ts";
import {
ConstantContext,
Neg_termContext,
NumberContext,
Rest_expressionContext,
Rest_termContext,
StatementContext,
} from "./CalcParser.ts";
export type CalcResult = {
result?: number;
};
export default class CalculatorListener implements CalcListener {
private calculatorStack: Array<Array<number>>;
private result: CalcResult;
constructor() {
this.calculatorStack = [];
this.result = {};
}
visitTerminal(_node: TerminalNode): void {
// do nothing
}
visitErrorNode(_node: ErrorNode): void {
// do nothing
}
enterEveryRule(_ctx: ParserRuleContext): void {
// do nothing
}
exitEveryRule(_ctx: ParserRuleContext): void {
// do nothing
}
private getLastFrame(): Array<number> | undefined {
return this.calculatorStack[this.calculatorStack.length - 1];
}
enterStatement(_ctx: StatementContext) {
this.calculatorStack.push([]);
}
exitStatement(_ctx: StatementContext) {
const frame = this.calculatorStack.pop();
if (this.calculatorStack.length === 0) {
if (frame?.length == 1) {
this.result.result = frame.pop();
return;
}
} else if (frame?.length === 1) {
const lastFrame = this.getLastFrame();
const r = frame.pop();
if (r !== undefined) {
lastFrame?.push(r);
return;
}
}
throw new Error("Unreachable");
}
exitRest_expression(ctx: Rest_expressionContext): void {
const op: string | undefined = ctx._op.text;
const lastFrame: Array<number> | undefined = this.getLastFrame();
const rear: number | undefined = lastFrame?.pop();
const prev: number | undefined = lastFrame?.pop();
switch (op) {
case "+":
if (rear != undefined && prev != undefined) {
lastFrame?.push(prev + rear);
} else {
throw new Error("Something wrong (addition)");
}
break;
case "-":
if (rear != undefined && prev != undefined) {
lastFrame?.push(prev - rear);
} else {
throw new Error("Something wrong (subtract)");
}
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Undefined operator : ${op}`);
}
}
exitRest_term(ctx: Rest_termContext): void {
const op: string | undefined = ctx._op.text;
const lastFrame: Array<number> | undefined = this.getLastFrame();
const rear: number | undefined = lastFrame?.pop();
const prev: number | undefined = lastFrame?.pop();
switch (op) {
case "*":
if (rear != undefined && prev != undefined) {
lastFrame?.push(prev * rear);
} else {
throw new Error("Something wrong (multiply)");
}
break;
case "/":
if (rear != undefined && prev != undefined) {
lastFrame?.push(prev / rear);
} else {
throw new Error("Something wrong (divide)");
}
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Undefined operator : ${op}`);
}
}
exitNeg_term(_ctx: Neg_termContext): void {
const lastFrame: Array<number> | undefined = this.getLastFrame();
const top: number | undefined = lastFrame?.pop();
if (top) {
lastFrame?.push(-top);
}
}
exitNumber(ctx: NumberContext): void {
const c: string = ctx.getText();
const lastFrame: Array<number> | undefined = this.getLastFrame();
lastFrame?.push(Number.parseFloat(c));
}
exitConstant(ctx: ConstantContext): void {
const c: string = ctx.getText();
const lastFrame: Array<number> | undefined = this.getLastFrame();
switch (c) {
case "π":
case "PI":
case "pi":
lastFrame?.push(Math.PI);
break;
case "e":
lastFrame?.push(Math.E);
break;
default:
throw new Error(`Unrecognized token : ${c}`);
}
}
}
그 다음 Calculator를 만듭시다.
import { CharStreams, CommonTokenStream, ParseTreeWalker } from "npm:antlr4";
import CalcLexer from "./CalcLexer.ts";
import CalcParser from "./CalcParser.ts";
import CalculatorListener from "./CalculatorListener.ts";
export default async function calculate(input: string): Promise<number> {
const validation = await validateInput(input);
if (validation) {
const charStream = CharStreams.fromString(input);
const lexer = new CalcLexer(charStream);
const tokens = new CommonTokenStream(lexer);
const parser = new CalcParser(tokens);
const listener = new CalculatorListener();
const tree = parser.statement();
ParseTreeWalker.DEFAULT.walk(listener, tree);
return listener.getResult();
}
throw new Error(`Invalid input : ${input}`);
}
async function validateInput(input: string): Promise<boolean> {
const validations = await Promise.all([
checkParenthesis(input),
]);
return validations.reduce((p, c) => p && c, true);
}
function checkParenthesis(input: string): boolean {
const parenthesisStack = [];
for (let c of input) {
if (c === "(") {
parenthesisStack.push(c);
}
if (c === ")") {
if (parenthesisStack.length === 0) {
return false;
}
parenthesisStack.pop();
}
}
return parenthesisStack.length === 0;
}
오… 테스트 만드는데 tabnine이 테스트케이스도 써주는데 시발 답을 다르게 만들어줌 ㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋㅋ
아니 6-2*3이 0이지 왜 5야… 여튼 테스트를 다음과 같이 만들었더니 잘 된다.
import { assertEquals } from "https://deno.land/std@0.204.0/assert/assert_equals.ts";
import calculate from "./Calculator.ts";
Deno.test(async function calculateTest() {
const result = await calculate("2+3")
assertEquals(result, 5);
})
Deno.test(async function calculateTest2() {
// Multiple operations test cases
const testCases = [
{ input: "2+3*4", output: 14 },
{ input: "6-2*3", output: 0 },
{ input: "10/2+5", output: 10 },
{ input: "(2+3)*4", output: 20 },
{ input: "(6-2)*3", output: 12 },
{ input: "10/(5-3)", output: 5 },
];
for (const testCase of testCases) {
const result = await calculate(testCase.input);
assertEquals(result, testCase.output);
}
});
잘된다.
오늘의 코드 : https://git.aosamesan.synology.me/aosamesan/deno-antlr-calc
답글 남기기